Maternity Leave in France: Expat Guide
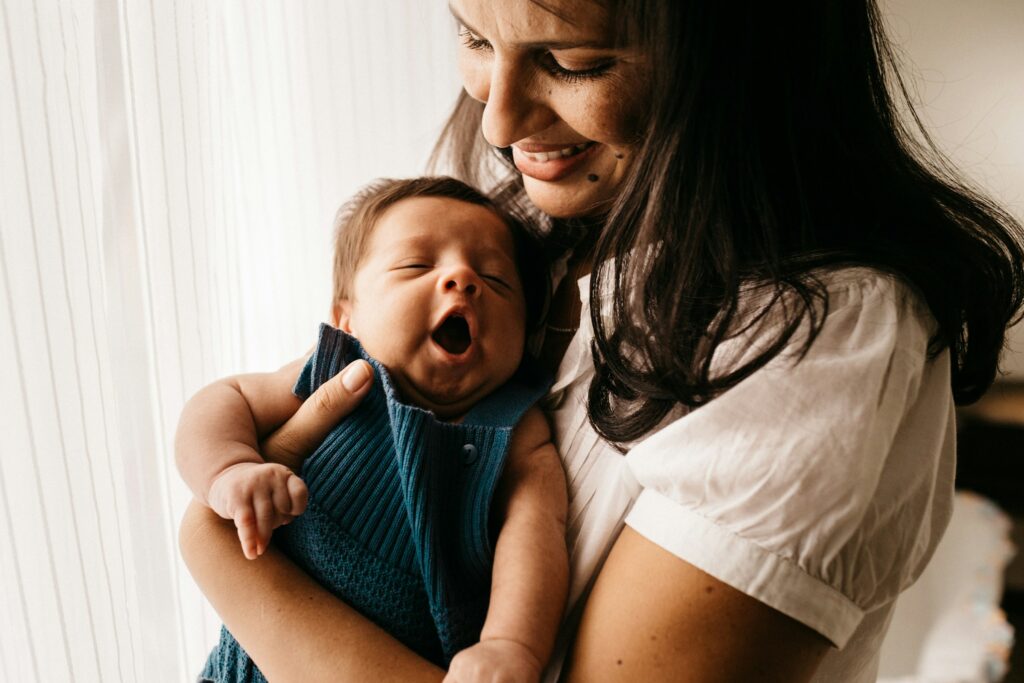
France is known for its strong worker protections and family-friendly policies, and maternity leave is no exception. Expats living and working in France can benefit from a generous maternity leave system that ensures financial support and job security during this important time.
However, understanding the specific rules, eligibility criteria, and application process can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with the French social security system. This guide covers everything expat parents need to know about maternity leave in France, from how long it lasts to how much they will be paid and how to apply.
Who is eligible for maternity leave in France?
In France, maternity leave is available to all employees, including expats, who meet specific criteria. To be eligible for maternity leave, you generally need to meet the following conditions:
- Employment – You must be an employee, whether full-time, part-time, or on a temporary contract. Freelancers or self-employed individuals might not be automatically entitled to maternity leave unless they contribute to the social security system in a similar way to employees.
- Social security contributions – To be eligible for maternity benefits, you need to have paid into France’s social security system (Sécurité Sociale). Expats who work in France and are registered with the social security system will be entitled to the same maternity benefits as French nationals.
- Minimum work requirement – To qualify for maternity leave, employees must have worked a minimum number of hours or days before the start of their leave. The minimum period varies depending on how long you’ve been employed and whether you’re a temporary worker or in a fixed-term contract.
- Length of residence – For non-EU expats, eligibility can also depend on your residence status and the length of time you’ve lived in France. If you’ve been employed and contributing to the French social security system, you should be entitled to maternity leave. However, it’s important to check specific residency requirements based on your nationality.
For most employees, including expats who meet these criteria, maternity leave is granted as a right, and the process of applying for it is relatively straightforward.
How much maternity leave do you get in France?
Maternity leave in France is designed to give ample time for recovery and bonding with the child, and it is among the most generous in Europe. The length of maternity leave you’re entitled to depends on various factors, such as how many children are expected and whether it’s your first pregnancy.
If it’s your first or second child, the standard maternity leave lasts 16 weeks, with six weeks taken before the due date and ten weeks following the birth. If you’re expecting twins, your maternity leave is extended to 34 weeks, with 12 weeks before the due date and 22 weeks after birth.
For your third or subsequent child, maternity leave lasts 26 weeks in total, with eight weeks taken before the due date and 18 weeks after birth.
If the baby is born prematurely or the mother experiences medical complications, maternity leave can be extended based on the advice of a doctor. In some cases, if more time is needed, additional parental leave may be taken, although this leave is not paid at the same rate as the maternity leave.
How much money do you get paid during maternity leave in France?
During maternity leave in France, mothers receive financial support through the French social security system. The amount paid is based on their average salary over the three months before the leave begins, with a cap set by social security.
Maternity benefits typically cover around 90% of the mother’s average salary, up to a maximum daily limit, which is adjusted annually. Employers do not usually pay this allowance directly, but some companies offer additional compensation so you can maintain a full salary, depending on contractual agreements or collective bargaining arrangements.
What paternity and parental leave is available in France?
In France, fathers are entitled to 28 days paternal leave, which includes four days that must be taken immediately after the birth and an additional 24 days that can be taken within six months. This leave is available to all employed fathers, including expats, as long as they are registered with the French social security system.
Paternity leave is paid by social security rather than the employer. The amount is calculated based on their average salary over the three months before the leave begins, with a cap set by social security. Typically, the amount given will be around 90% of the salary, with a quarterly cap currently at around €10,000. Some employers offer additional compensation to maintain a full salary during paternity leave, but this will depend on the employment contract.
In addition to maternity and paternity leave, France offers parental leave, which allows either parent to take time off to care for their child. This leave can last up to three years per child and can be taken full-time or part-time. Whilst parental leave is not fully paid, parents may receive financial support from the Caisse d’Allocations Familiales (CAF), depending on their income and employment situation. This system provides flexibility for parents who wish to extend their time at home with their child beyond the standard maternity or paternity leave.
How do you apply for maternity leave in France?
To apply for maternity leave in France, you must inform your employer in writing, providing the expected due date and the planned start date of your leave. While there is no strict legal deadline for notifying an employer, it is recommended to do so at least a few months in advance to allow proper arrangements to be made. The employer might request a medical certificate confirming the pregnancy and expected due date.
In addition to notifying your employer, you must also inform the French social security system (CPAM) so you can receive your maternity benefits. This will require you to submit proof of your pregnancy, usually a medical certificate, along with details of your employment and earnings. The social security office will then calculate the maternity allowance based on your salary and ensure payments are made throughout the leave period.
If you are self-employed or not on a standard employment contract, you must still notify Social Security and may need to provide additional documents regarding your income and contributions. In all cases, it’s best to start the process as early as possible to avoid any delays.
Moving to the France? Expatriate Group provides flexible and comprehensive health insurance policies, specifically designed for expats, including international family health insurance. Get a quote today.